Deploying open-source SOC lab with red team simulation, at home. Elasticsearch Stack EDR + SIEM (Part 1)
Introduction
I’m always want to
have my own lab that can mimic enterprise monitoring at home which include EDR
(Endpoint Detection and Response), SIEM (Security Information and Event
Management), case management and have a threat intel platform. It must be something
that can be built from open source and free...
Since there is significant upgrade on my personal workstation, I’m able to ramp up my virtualization capacity to support my endeavor.
let’s gooooo!
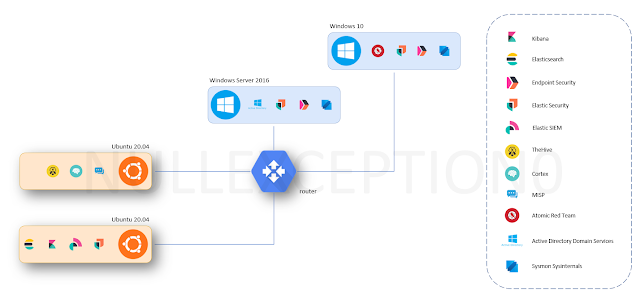
Network & Resources
Allocation
For this lab, everything will be deployed in virtual machine (VM) and in private network, simple. These are minimum specification I used in this lab; you can allocate more if you have more resources.
- CPU: 2 cores
- Network: bridged connection and replicate physical network connection state
- Storage: 80 GB
- RAM: 8 GB (For both Ubuntu VM, I’m allocating 16GB for better performance)
Architectural &
System Design
Refer to the diagram
above
We will deploy two (2)
Ubuntu 20.04 Desktop as a Server (ya, ya, ya... GUI noob bla bla bla). One to
host Elastic SIEM server as stand-alone server. Another one to host TheHive,
Cortex and MISP. For easy access, we will install and enable OpenSSH Server.
So, long story short,
I’m very intrigue by latest Elastic Security that have SIEM and Endpoint
Security that allow collection of logs, threat detection and response. So, SIEM
+ EDR. We will install and enable Fleet to manage and deploy our Elastic Agent.
Elastic Agent is pretty neat, variety of log can be collected via single agent
depending on your integration and policy. Furthermore, it also acts as our EDR
agent.
If you want more
headache and heartache, we can send alert or generate case to TheHive by using Webhook
Web API connector, but we need to change the rule to make this happen, it depends
on you. I found no easy solution on this…. yet. Might need to create a script
to add connector to the rule in bulk. Hopefully, someday Elastic will do
something about it. One of the features in the Elastic Security is that you can
create case based on alert and event triggered from Elastic SIEM, when you
create a case, you can send that case to your case management solution via
connector. Unfortunately, Webhook connector is not available for integration, if not we can directly send new cases to TheHive. Kalau
tak memang senang kerja.
In term of case
management platform, we will use TheHive and it will be integrated with Cortex
and MISP. Why I choose to use this? So basically, TheHive is centralize console
where we can create case, track and collaborate to solve the case and analyze
any observable or indicator of compromise during the investigation of the case,
integration with Cortex and MISP makes incident response efficient and faster.
We will use Cortex for
its Analyzer, Cortex Analyzer allow analyst/user to grab information from TI
platform, Sandbox, Multi AV, IP reputation platform to analyze observable/IOC
found during analysis of the case with ease and minimal effort. By the way, some
Cortex Analyzer require to have API key to enable. MISP as threat intel feed platform,
we will integrate it with Cortex Analyzer.
For Windows Server
2016, you can download evaluation version, I choose to install Windows Server
2016 Datacenter with Desktop Experience to get full features (because I have
only this iso at the moment). We will install and enable Active Directory Domain
Services (ADDS). Any Window Server version is ok for this lab, we just need
ADDS for group policy objects (GPO), user and computer management. ADDS is also
requirement in some of Atomic Red Team modules.
For victim pc, I use
Windows 10 Pro, we will install Atomic Red Team to run attack simulation based
on MITRE ATT&CK framework, so we can learn attacker tactics, techniques,
and procedures. I’m very much interested on what tools & command will be
used in the simulation.
Both Windows machines
will have Sysmon, Elastic Agent installed.
This installation is
for closed environment. It is not advisable to perform this for production
environment and only setup this lab in environment you have permission only.
Tips:
- It is advisable to make snapshot for every successful installation. Just in case, in the moment of failure, you can revert back to last known working state.
- To make sure your snapshot is working when you revert back, power off your machine before making your snapshot.
- When certain component is failed to run, restart the service or check you configuration file. If failed and you want to remove the package, use purge option. This will remove the configuration files too, revert back to last working state save more time and less of a hassle.
Installing Ubuntu
Elastic SIEM EDR Server
Switch to an
interactive session as a root user so we don’t need to put sudo in every command
we run.
|
sudo -i |
|
apt update -y apt upgrade -y |
|
apt install net-tools
curl apt-transport-https openssh-server -y |
|
ifconfig |
Best is to configure you server network configuration
into static IP address, dynamic address might break your app during runtime when the IP address
changed.
Enable OpenSSH-Server on
startup and start OpenSSH-Server
|
systemctl enable openssh-server.service systemctl start
openssh-server.service |
Now you can access this server by using ssh. I prefer
this way. Most of the time, I ssh to this server via Windows terminal.
Download and install
Elasticsearch PGP Key
|
wget -qO - https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
| gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/elasticsearch-keyring.gpg |
|
echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/elasticsearch-keyring.gpg]
https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/7.x/apt stable main" | tee
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/elastic-7.x.list |
|
apt update -y |
|
apt install kibana elasticsearch elastic-agent -y |
|
nano /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml |
|
node.name: node-1 network.host: 192.168.1.104 |
Save and close the file.
To
enable
Elasticsearch on startup and start Elasticsearch
|
systemctl
daemon-reload systemctl enable
elasticsearch.service systemctl start
elasticsearch.service |
|
curl 192.168.1.104:9200 |
|
{ "name" :
"node-1", "cluster_name"
: "elasticsearch", "cluster_uuid"
: "YlxaYzpeTrCcDqBaPg_Ecg", "version" : { "number" :
"7.17.1",
"build_flavor" : "default", "build_type"
: "deb", "build_hash"
: "e5acb99f822233d62d6444ce45a4543dc1c8059a", "build_date"
: "2022-02-23T22:20:54.153567231Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "8.11.1",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "6.8.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" :
"6.0.0-beta1" }, "tagline" :
"You Know, for Search" } |
Configuring
Elasticsearch and Kibana SSL Certicate and Elastic XPack
Next, create YAML file at /usr/share/elasticsearch/instances.yml
to configure certificate creation for SSL and configure X-Pack
|
nano /usr/share/elasticsearch/instances.yml |
|
instances: - name:
"elasticsearch" ip: -
"192.168.1.104" - name:
"kibana" ip: -
"192.168.1.104" |
|
/usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-certutil cert ca
--pem --in instances.yml --out certs.zip |
|
unzip /usr/share/elasticsearch/certs.zip -d
/usr/share/elasticsearch/ |
Create folder for Elasticsearch and
Kibana cert
|
mkdir /etc/elasticsearch/certs/ca -p mkdir /etc/kibana/certs/ca -p |
|
cp /usr/share/elasticsearch/ca/ca.crt
/etc/elasticsearch/certs/ca cp /usr/share/elasticsearch/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.crt
/etc/elasticsearch/certs cp /usr/share/elasticsearch/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.key
/etc/elasticsearch/certs chown -R elasticsearch: /etc/elasticsearch/certs chmod -R 770 /etc/elasticsearch/certs |
|
cp /usr/share/elasticsearch/ca/ca.crt /etc/kibana/certs/ca cp /usr/share/elasticsearch/kibana/kibana.crt /etc/kibana/certs cp /usr/share/elasticsearch/kibana/kibana.key /etc/kibana/certs chown -R kibana: /etc/kibana/certs chmod -R 770 /etc/kibana/certs |
|
nano /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml |
|
# ---------------------------------- Security
---------------------------------- # xpack.security.enabled: true xpack.security.transport.ssl.enabled: true xpack.security.transport.ssl.verification_mode: certificate xpack.security.transport.ssl.key:
/etc/elasticsearch/certs/elasticsearch.key xpack.security.transport.ssl.certificate:
/etc/elasticsearch/certs/elasticsearch.crt xpack.security.transport.ssl.certificate_authorities: [
"/etc/elasticsearch/certs/ca/ca.crt" ] # xpack.security.http.ssl.enabled: true xpack.security.http.ssl.verification_mode: certificate xpack.security.http.ssl.key:
/etc/elasticsearch/certs/elasticsearch.key xpack.security.http.ssl.certificate:
/etc/elasticsearch/certs/elasticsearch.crt xpack.security.http.ssl.certificate_authorities: [
"/etc/elasticsearch/certs/ca/ca.crt" ] |
Next,
we need to create and generate password for all built-in users and roles for
Elasticsearch. We will use elasticsearch-setup-passwords to do this. Make sure
to save the output and store the credential somewhere safe. We need this
password to configure configuration for Kibana later.
This
command will execute elasticsearch-setup-passwords, display the output to the
terminal and redirect the output to store in /home/elastic-cred.txt
|
/usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-setup-passwords
auto | tee /home/elastic-cred.txt |
Configured
and enable Elastic XPACK, SSL and configuration for Kibana in
/etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml file
|
nano /etc/kibana/kibana.yml |
Uncomment,
change and add the following:
|
# Change to you host IP Address # Specifies the address to which the Kibana
server will bind. IP addresses and host names are both valid values. # The default is 'localhost', which usually
means remote machines will not be able to connect. # To allow connections from remote users,
set this parameter to a non-loopback address. server.host: "192.168.1.104" # Change to you host IP Address # The URLs of the Elasticsearch instances to
use for all your queries. elasticsearch.hosts:
["https://192.168.1.104:9200"] # If your Elasticsearch is protected with
basic authentication, these settings provide # the username and password that the Kibana
server uses to perform maintenance on the Kibana # index at startup. Your Kibana users still
need to authenticate with Elasticsearch, which # is proxied through the Kibana server. xpack.security.enabled: true elasticsearch.username: "elastic" elasticsearch.password:
"your-elastic-password-here- refer-to-elastic-cred.txt" # to enable detection xpack.encryptedSavedObjects.encryptionKey:
"add-32-random-character-here" # Enables SSL and paths to the PEM-format
SSL certificate and SSL key files, respectively. # These settings enable SSL for outgoing
requests from the Kibana server to the browser. server.ssl.enabled: true server.ssl.certificate:
"/etc/kibana/certs/kibana.crt" server.ssl.key:
"/etc/kibana/certs/kibana.key" # Optional settings that provide the paths
to the PEM-format SSL certificate and key files. # These files are used to verify the identity
of Kibana to Elasticsearch and are required when #
xpack.security.http.ssl.client_authentication in Elasticsearch is set to
required. elasticsearch.ssl.certificate:
"/etc/kibana/certs/kibana.crt" elasticsearch.ssl.key:
"/etc/kibana/certs/kibana.key" # Optional setting that enables you to
specify a path to the PEM file for the certificate # authority for your Elasticsearch instance. elasticsearch.ssl.certificateAuthorities:
["/etc/kibana/certs/ca/ca.crt"] |
Save and close the file.
Restart
Kibana
|
systemctl restart elasticsearch.service |
|
systemctl
daemon-reload systemctl enable kibana.service systemctl start kibana.service |
Once
you have login. From your dashboard, navigate to Stack Management.
Navigate to Stack Management > Security > Users. Click on Create User.
Let’s create new user named analyst, we will set this account privileges as superuser. Therefore, we do not need to use account elastic in the future to manage this stack. Better that way, because under the hood, elastic user account is important account that being used to managed Elasticsearch & Kibana functionality, if you remove or change this account password, you will break the stack! I learned it hard way.
After finished with all the details, click on Create user button. The user will be created. Next, log out and login back to the Kibana using this newly create user account. We will use this account to manage and configuring settings in Kibana and so on.
Enable Trial License
Next,
we need to enable Trial License so we can try additional features such as
Webhook API, enterprise rule and many more.
Navigate
to Stack Management > License management.
Activate 30-day trial by click on Start trial.
Click on Start my trial. Done!
Kibana
will reload, we can move on to next step.
Add Fleet server
Before
we can add elastic agent into our endpoint, we need to enable Fleet server.
Navigate
to Management > Fleet
Click
on Fleet Settings. This will pop up side panel. Configure as follow. Change the
IP Address to your host IP Address.
Fleet
Server hosts: https://<your-ip>:8220
Elasticsearch
hosts: https://<your-ip>:9200
Save
and apply settings.
Then
you will be back to Fleet Agents page.
Here
you just need to click on Generate service token only.
Once
the token has generated, you will be provided with step to installed &
start your Fleet server. Save this service token for future use.
So
back to terminal. Paste this command to start installing the Fleet server.
Follow format provided.
|
sudo elastic-agent enroll
--url=https://<your-ip>:8220 \
--fleet-server-es=https:// <your-ip>:9200 \
--fleet-server-service-token=<your-service-token> \
--fleet-server-policy=<fleet-server-policy> \
--certificate-authorities=/etc/elasticsearch/certs/ca/ca.crt \
--fleet-server-es-ca=/etc/elasticsearch/certs/ca/ca.crt \
--fleet-server-cert=/etc/elasticsearch/certs/elasticsearch.crt \
--fleet-server-cert-key=/etc/elasticsearch/certs/elasticsearch.key |
It
is something like this. Here we will reuse Elasticsearch certificate for better
cert management... hehe
|
sudo elastic-agent enroll --url=https://192.168.1.104:8220 \ --fleet-server-es=https://192.168.1.104:9200 \ --fleet-server-service-token=AAEAAWVsYXN0aWMvZmxlZXQtc2VydmVyL3Rva2VuLTE2NDg2NDMyOTA3ODI6a04tNkRSMUdUNDZ6LVd5V1Zvc0lIQQ \ --fleet-server-policy=499b5aa7-d214-5b5d-838b-3cd76469844e \ --certificate-authorities=/etc/elasticsearch/certs/ca/ca.crt \ --fleet-server-es-ca=/etc/elasticsearch/certs/ca/ca.crt \ --fleet-server-cert=/etc/elasticsearch/certs/elasticsearch.crt \ --fleet-server-cert-key=/etc/elasticsearch/certs/elasticsearch.key |
*no need to add sudo if you in root session.
The
output should show something like this:
To
enable
Elastic-Agent on startup
|
systemctl
daemon-reload systemctl enable
elastic-agent.service reboot |
So,
wait until Kibana and Elasticsearch back online, login and browse back to Fleet
page.
Tada!
Our Fleet server installation and enrolment is done. You may inspect your
Server enrolment.
We
finally can create new agent policy, make integration policies, manage agent
and policy.
Create
new agent policy for Windows Agent
Navigate
to Management > Fleet > Agent Policies. Click on Create Agent Policy.
To
add integration, click on add integration.
Here
there is two (2) option you can use to go to Add Integration. First, from side
panel. Second, from homepage.
Once
you in Integrations page. First, we will enable Endpoint Security. Click on
Endpoint Security.
Click
Add Endpoint Security.
Save
and continue.
Click
on Add Elastic Agent later.
This
is the step to add integration into your policy. Add more relevant integration
to your policy for example:
- Endpoint Security
- Prebuilt Security
Detection Rules
- Windows
- System
We
are done on Elastic SIEM and EDR Configuration. The only thing needs to do now
is to enroll agent to Windows machine to start monitoring and receiving data
from our endpoint.
Installing
Elastic Agent on Endpoint
For
this lab, we will skip this step until the Windows 10 machine has been
installed with Atomic Red Team Framework and have join the Active Directory. If
not, Elastic Security will block the installation of Atomic Red Team.
We
need to installed Elasticsearch Certificate Authority that we generate
previously to the Trusted Root Certification Authorities store before we can
successfully enroll the agent to the Elasticsearch Fleet server. We will do this
via Group Policy Objects (GPO), so it’s much easier for us to distribute the CA
certificate on all the endpoint.
Once
the above activities have been performed, generally, the following is how you
can install and start elastic agent on the endpoint. Installing Elastic Agent
on endpoint is pretty straight forward.
First
download the Elastic Agent binary from Elasticsearch website into your endpoint:
https://www.elastic.co/downloads/past-releases/elastic-agent-7-17-1
Download
the binary based on your platform.
Login
into Kibana, navigate to Fleet > Agents > Add Agents
For
this enrolment, I’m using policy name Windows, you can observe that I have add
4 integrations to the policy.
This
pop-up shows step by step guideline to install the agent on your endpoint.
Copy
the command line under step number 3.
Start
new command-line console in your endpoint with Administrator privilege,
navigate to the folder where the Elastic Agent binary is located.
Execute
the command-line you copied before.
Once
the installation is complete, you will see the agents register to your Fleet
Agents Dashboard, at the same time, it also has sent log to the SIEM and
monitor your endpoint.
*The
picture is bit different because this is from my other lab, but you get what I
mean.
So, that’s how you enroll Elastic Agent to the endpoint.
Next, we
will do for another setup for MISP, Cortex and TheHive server. Follow along in
another post.


























Nice SOC solutions
ReplyDeleteWaiting for Part 2 !!
ReplyDeleteThanks
ReplyDelete